How to operate a drone safely and effectively opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of drone operation, encompassing pre-flight checks, control mechanisms, flight planning, image capture, troubleshooting, and post-flight maintenance. We’ll cover everything from mastering the controls to understanding and adhering to relevant regulations, ensuring you can confidently and responsibly take to the skies.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide offers a structured approach to learning, incorporating practical advice and clear explanations. By following these steps, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the intricacies of drone flight and capture stunning aerial footage.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount. This ensures the safety of both the drone and its surroundings, preventing potential accidents and ensuring smooth operation.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection is crucial for identifying any potential issues before takeoff. This involves a visual check of all major components and their functionality. The following table Artikels key aspects of this inspection:
| Component | Inspection Item | Acceptable Condition | Unacceptable Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Visual inspection for cracks, chips, or damage | No visible damage; blades firmly attached | Cracks, chips, or significant wear; loose blades |
| Battery | Check battery level and condition | Sufficient charge; no visible damage or swelling | Low charge; visible damage or swelling |
| Motors | Visual inspection for damage or obstructions | No visible damage; free from obstructions | Visible damage; obstructions present |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Check for smooth movement and proper function | Smooth movement in all directions; no binding | Jerky movement; binding or malfunction |
Understanding Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone requires awareness of local regulations and airspace restrictions. Failure to comply can lead to fines or legal repercussions. Check with your local aviation authority (e.g., FAA in the US, CAA in the UK) for specific rules and regulations in your area. Many apps and websites provide airspace maps that highlight restricted zones.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedures
A safe takeoff and landing are essential for preventing accidents. Always choose a level, open area away from obstacles. Ensure the drone has a clear path for ascent and descent. A smooth, controlled takeoff and landing minimizes the risk of damage.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS.
- Perform a pre-flight check of all systems.
- Slowly lift the drone vertically to a safe height.
- For landing, slowly descend the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Handling Unexpected Situations
Unexpected situations, such as low battery or GPS signal loss, can occur during flight. A well-defined decision-making process is crucial for handling such events safely.
(Flowchart would be inserted here. A textual description is difficult to represent the visual nature of a flowchart, but it would show decision points such as low battery – land immediately; GPS signal loss – return to home point; etc.)
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding drone controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different drones may have varying control mechanisms, but the core principles remain consistent.
Drone Control Types and Functionalities
Most drones utilize joysticks for primary control, offering precise maneuvering. Some drones incorporate touchscreen interfaces for additional settings and camera control. Joysticks generally control altitude, direction, and camera tilt, while touchscreens offer access to more advanced features and settings.
Flight Modes
Various flight modes cater to different skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner mode typically limits speed and responsiveness, enhancing stability. Sport mode unlocks higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, demanding greater skill and caution.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control.
- Sport Mode: Enables higher speeds and more agile maneuvers.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and autonomous features.
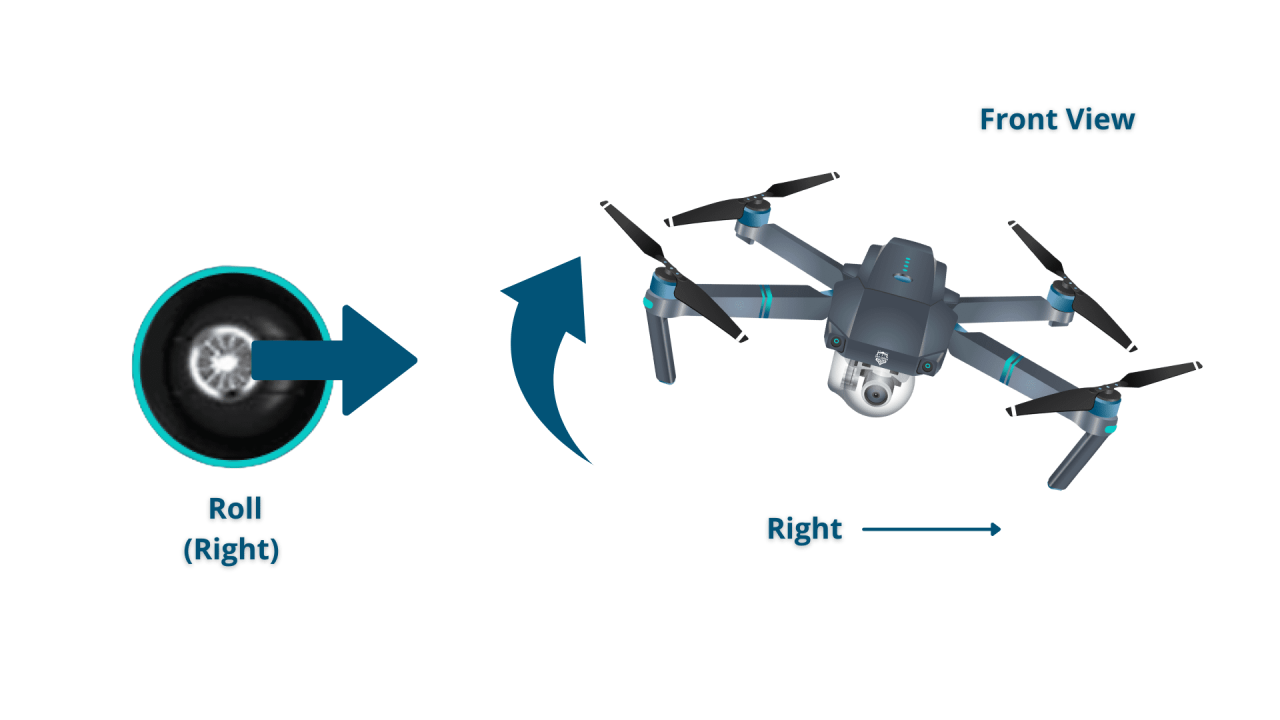
Drone Maneuvers
Mastering basic drone maneuvers is essential. These include hovering (maintaining a fixed position), ascending and descending (changing altitude), yawing (rotating left or right), pitching (tilting forward or backward), and rolling (tilting left or right).
Remote Controller Functions
A typical drone remote controller features various buttons and switches. Understanding their functions is crucial for safe and effective control.
| Button/Switch | Function |
|---|---|
| Left Joystick | Controls yaw and throttle |
| Right Joystick | Controls pitch and roll |
| Return to Home (RTH) Button | Initiates an automated return to the home point |
| Camera Control Buttons | Adjust camera settings (e.g., zoom, photo/video capture) |
| Power Switch | Turns the controller on and off |
Flight Planning and Mission Execution
Effective flight planning is essential for successful aerial photography and videography missions. This involves defining waypoints, setting altitudes, and considering factors like battery life and airspace restrictions.
Sample Flight Plan
A simple aerial photography mission might involve capturing images of a building from various angles. The flight plan could include waypoints around the building at a consistent altitude, allowing for overlapping shots for potential photogrammetry or creating a panorama.
(Specific GPS coordinates and altitudes would be included here for a real-world example, but these are omitted due to the lack of a specific location for the example.)
Battery Management and Flight Time, How to operate a drone
Accurate battery management is critical. Always calculate flight time based on the drone’s specifications and environmental factors (wind, temperature). It’s recommended to always have a spare battery available.
Using GPS Coordinates
Many drone apps allow for flight path planning using GPS coordinates. This enables precise control over the drone’s movement, especially useful for complex missions or repeatability.
Safe Return to Home
The Return-to-Home (RTH) function is a safety feature that automatically guides the drone back to its starting point. However, always monitor the drone’s return, especially in challenging conditions.
- Initiate RTH function on the controller.
- Monitor the drone’s return path.
- Be prepared to take manual control if necessary.
- Land the drone safely once it reaches the home point.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone’s camera is a key component for capturing stunning aerial footage. Understanding camera settings and composition techniques is essential for achieving high-quality results.
Camera Settings
Drone cameras offer various settings that affect image quality. ISO controls sensitivity to light, shutter speed determines exposure time, and aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens. Adjusting these settings allows for optimization in different lighting conditions.
Optimizing Settings for Different Lighting
In bright sunlight, a lower ISO and faster shutter speed might be necessary to prevent overexposure. In low-light conditions, a higher ISO and slower shutter speed might be required, though this may introduce more noise.
Composition Techniques
Effective composition is crucial for compelling aerial photography and videography. Techniques such as the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry can enhance the visual appeal of your images.
Post-Flight Image Review

After each flight, review captured images and videos to ensure quality and completeness. Check for sharpness, proper exposure, and any technical issues.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as takeoff and landing procedures, is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
- Check for sharpness and focus.
- Assess exposure and lighting.
- Review for any technical artifacts (e.g., noise, distortion).
- Ensure sufficient coverage and desired angles.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful planning and operation, drone malfunctions can occur. Understanding common issues and troubleshooting steps is essential for resolving problems efficiently and safely.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Common problems include low battery, GPS signal loss, motor failure, and communication issues. These can be caused by various factors, such as depleted batteries, interference, or mechanical damage.
Troubleshooting Steps

Troubleshooting involves systematically checking components and addressing potential causes. For example, low battery requires immediate landing and battery replacement. GPS signal loss may necessitate relocating to an area with better signal reception.
Interpreting Error Messages
Drone controllers and apps often display error messages providing clues to the problem. Understanding these messages is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Preventing Drone Issues
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning propellers and checking motor mounts, can prevent many common issues. Storing the drone properly also helps maintain its functionality and lifespan.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are essential for extending the lifespan and ensuring the continued reliable operation of your drone.
Drone Storage and Maintenance
After each flight, store the drone in a clean, dry place, away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight. Regularly inspect and clean all components, paying attention to propellers, motors, and the camera lens.
Essential Maintenance Tools and Supplies
A basic toolkit should include a cleaning cloth, compressed air, and a small screwdriver set. Additional tools may be necessary depending on the drone model and any specific maintenance requirements.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and longevity. This might involve weekly inspections, monthly cleaning, and periodic more in-depth checks.
- Weekly: Visual inspection for damage, cleaning propellers.
- Monthly: Thorough cleaning of all components.
- Quarterly: More in-depth inspection of motors, gimbal, and other critical components.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical skill and responsible awareness. From meticulous pre-flight preparations to understanding airspace restrictions and maintaining your equipment, each step contributes to a safe and successful flight experience. By diligently following the guidelines Artikeld in this guide and prioritizing safety, you’ll not only capture incredible aerial footage but also contribute to the responsible development of the drone industry.
FAQ Resource
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a significantly different location.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal during flight?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If not available, carefully bring the drone down manually, prioritizing a safe landing area.
How do I handle strong winds?
Avoid flying in strong winds. If caught unexpectedly, land the drone immediately. Consult your drone’s manual for wind tolerance limits.
